Bangladesh, nestled in South Asia, has experienced an extraordinary transformation over the past few decades. Once predominantly reliant on agriculture, the country has swiftly transitioned into a dynamic economy marked by rapid industrialization and impressive economic growth. This evolution has positioned Bangladesh as one of the fastest-growing economies on the global stage, attracting significant attention from investors, policymakers, and analysts worldwide.
The shift from an agrarian economy to one characterized by robust industrial activities reflects a broader trend of modernization and economic diversification. This transformation has been driven by several factors, including strategic investments, policy reforms, and an increasingly skilled workforce. The growth of key sectors such as textiles and garments, information technology, and services has played a pivotal role in this economic metamorphosis.
As Bangladesh strides into the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it finds itself at a crossroads where traditional industrial practices meet cutting-edge technologies. The Fourth Industrial Revolution, often referred to as Industry 4.0, is defined by the integration of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics into industrial processes. For Bangladesh, this era represents both unprecedented opportunities and formidable challenges.
The integration of these technologies promises to enhance productivity, streamline operations, and foster innovation across various sectors. However, it also necessitates a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, how the workforce is trained, and how infrastructure is developed. The rapid pace of technological advancement means that Bangladesh must navigate a complex landscape of emerging trends while addressing existing economic and social challenges.
This transformative period is marked by significant changes in the country’s industrial landscape, including the adoption of advanced manufacturing processes, the rise of tech-driven start-ups, and the digitalization of services. As Bangladesh embraces these changes, it faces a unique set of challenges that will influence its economic trajectory and future development. Addressing these challenges effectively will be crucial for ensuring sustainable growth and maximizing the benefits of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In summary, Bangladesh’s remarkable journey from an agrarian economy to a burgeoning industrial powerhouse underscores its resilience and adaptability. As the country advances into the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it stands poised to leverage new technologies and innovations to further enhance its economic growth. However, navigating the accompanying challenges will require concerted efforts from all sectors of society, including government, business, and education, to ensure a balanced and prosperous future.
As Bangladesh continues its ascent into this new industrial era, it must also focus on fostering a supportive ecosystem for innovation and technological advancement. This includes enhancing research and development capabilities, improving access to digital infrastructure, and nurturing a culture of entrepreneurship. Investment in education and vocational training will be critical to equipping the workforce with the skills needed to thrive in a technology-driven economy.
Additionally, Bangladesh must address infrastructural bottlenecks and streamline regulatory frameworks to create an environment conducive to business growth and technological integration. The government’s role in supporting industrial growth through strategic policies, incentives for technological adoption, and fostering public-private partnerships will be crucial.
Moreover, the emphasis on sustainable development must remain a priority. As the country industrializes, balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship will be essential to ensure that progress does not come at the expense of the planet’s health. Implementing green technologies, promoting energy efficiency, and addressing environmental challenges will help Bangladesh achieve sustainable and inclusive growth.
In navigating this transformative phase, Bangladesh has the opportunity to solidify its position as a leading economy in the global arena. By embracing technological advancements, overcoming challenges, and harnessing the potential of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the country can pave the way for long-term prosperity and development. The journey ahead will require resilience, adaptability, and a forward-thinking approach to fully realize Bangladesh’s economic potential and secure its place in the evolving global economy.
Economic Growth in Bangladesh
Bangladesh’s economic growth over the past two decades has been nothing short of impressive. The country has achieved an average annual GDP growth rate of approximately 6-7%, reflecting a robust expansion of various sectors. Key drivers of this growth include:
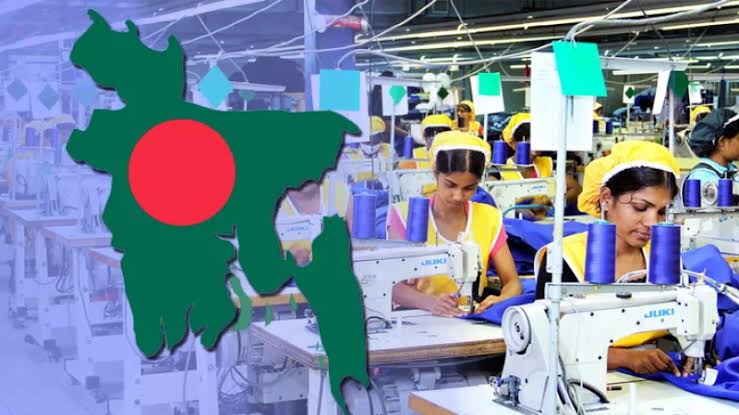
1. **Textiles and Garments Industry**: The textile and garments sector has been the linchpin of Bangladesh’s economic success. As one of the largest exporters of ready-made garments (RMG) in the world, the sector has generated significant foreign exchange earnings and employment opportunities. The industry’s growth has been fueled by competitive labor costs, favorable trade agreements, and investments in manufacturing capabilities.
2. **Services Sector**: The services sector has expanded rapidly, contributing substantially to GDP growth. Key sub-sectors such as financial services, telecommunications, and information technology (IT) have experienced significant development. The proliferation of digital services, including mobile banking and e-commerce, has further accelerated the growth of the services sector.
3. **Infrastructure Development**: Investments in infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and urban development, have supported economic activities and improved connectivity. Major projects such as the Padma Bridge, Dhaka Metro Rail, and expansion of port facilities have enhanced logistics and transportation efficiency.
4. **Remittances**: Remittances from Bangladeshi expatriates working abroad have been a crucial source of foreign exchange and have supported domestic consumption and investment. Remittances contribute to economic stability and play a vital role in improving living standards for many families.
The New Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, represents a transformative shift in industrial practices through the integration of digital technologies. For Bangladesh, this revolution brings both opportunities and challenges:
1. **Technological Advancements**: The adoption of advanced technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing traditional industries. In the textile sector, automation is enhancing production efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality. Other sectors, including manufacturing and agriculture, are also benefiting from technological innovations.
2. **Innovation and Start-ups**: Bangladesh has witnessed a surge in start-ups and innovation hubs that are driving entrepreneurial activity. The rise of tech start-ups and innovation centers has fostered a culture of creativity and problem-solving. These ventures are contributing to the development of new products, services, and business models.
3. **Digital Transformation**: The digitalization of various sectors is reshaping business practices and creating new opportunities. The fintech industry, in particular, has experienced rapid growth, with digital payment systems, mobile banking, and blockchain technology gaining traction. E-commerce platforms are also expanding, offering new avenues for trade and commerce.
4. **Green Technologies**: The focus on sustainable practices and green technologies is gaining momentum. The adoption of renewable energy sources, energy-efficient technologies, and eco-friendly practices is addressing environmental concerns and promoting sustainable development. Initiatives such as solar energy projects and green building practices are contributing to the country’s environmental goals.
Current Challenges
Despite the positive economic trends and the potential of the new industrial revolution, Bangladesh faces several challenges that must be addressed to sustain growth and development:
1. **Infrastructure Constraints**: While significant progress has been made, there are still gaps in infrastructure, particularly in transportation, energy, and urban development. Infrastructure bottlenecks can hinder economic activities, affect logistics, and limit the country’s competitiveness. Continued investment in infrastructure is essential for supporting growth and attracting foreign investment.
2. **Skill Gap**: The rapid pace of technological advancement requires a workforce with the necessary skills to adapt to new technologies. There is a need for investment in education and vocational training to bridge the skill gap and ensure that workers are equipped to meet the demands of Industry 4.0. Collaboration between educational institutions, businesses, and government agencies is crucial for developing a skilled workforce.
3. **Regulatory Environment**: The regulatory framework can sometimes pose challenges for businesses. Complex regulations, bureaucratic hurdles, and inconsistencies in enforcement can affect the ease of doing business. Streamlining regulations, improving transparency, and simplifying procedures are important for creating a conducive business environment and fostering investment.
4. **Environmental Concerns**: Rapid industrialization and economic growth have led to environmental challenges, including pollution, deforestation, and resource depletion. Ensuring sustainable development and addressing environmental issues are critical for long-term economic stability. Effective environmental policies and practices are needed to mitigate the impact of industrial activities on natural resources.
5. **Global Economic Uncertainty**: Bangladesh’s economy is influenced by global economic fluctuations and geopolitical tensions. Changes in global trade policies, economic slowdowns, and geopolitical conflicts can impact export-oriented industries and overall economic stability. Diversifying export markets and building economic resilience are important strategies for mitigating external risks.
Prospects and Opportunities
Looking ahead, Bangladesh has several prospects and opportunities to capitalize on:
1. **Increased Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)**: With ongoing reforms and improvements in the business environment, Bangladesh is well-positioned to attract more foreign investment. Sectors such as manufacturing, IT, and infrastructure offer significant opportunities for FDI. Creating a favorable investment climate and enhancing investor confidence will be key to attracting global investors.
2. **Expansion of Export Markets**: Diversifying export markets and products can help reduce dependency on traditional sectors and enhance economic resilience. Exploring new markets, particularly in emerging economies, and adding value to export products can boost competitiveness and growth.
3. **Development of Human Capital**: Investing in education and skills development is crucial for leveraging the benefits of new technologies and driving innovation. Strengthening the education system, promoting STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education, and fostering a culture of lifelong learning are important for building human capital.
4. **Sustainable Development**: Emphasizing sustainable practices and green technologies will not only address environmental concerns but also create new business opportunities. Promoting eco-friendly industries, renewable energy projects, and sustainable agriculture can contribute to long-term economic growth and environmental protection.
5. **Regional Integration**: Strengthening regional economic ties and participating in regional trade agreements can open up new markets and opportunities for Bangladesh. Engaging in regional cooperation, trade agreements, and cross-border infrastructure projects can enhance connectivity and economic integration.
Bangladesh’s journey of economic growth and industrial transformation is characterized by both achievements and challenges. The new industrial revolution presents significant opportunities for further development, but addressing current challenges is essential for realizing its full potential. By focusing on infrastructure development, skill enhancement, regulatory improvements, and sustainable practices, Bangladesh can continue its trajectory of growth and emerge as a key player in the global economy. The country’s ability to navigate these challenges and seize opportunities will determine its future economic success and its role in the evolving global landscape.
 A.B.M. Abir
A.B.M. Abir