This report delves into the reasons behind the delays in these mega projects, their current status, and the challenges that continue to hinder their progress. It also explores the implications of these delays for Bangladesh’s long-term growth trajectory and offers insight into potential solutions for more effective project implementation.
The Importance of Mega Projects in Bangladesh’s Development
Mega projects are crucial for Bangladesh’s infrastructure development, economic growth, and regional connectivity. Projects like the Padma Bridge, the Dhaka Metro Rail, the Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant, and the Payra Deep Sea Port are expected to provide long-term benefits by enhancing connectivity, improving energy security, and facilitating trade. They are integral to the government’s vision of transforming Bangladesh into a middle-income country and ultimately achieving the status of a developed nation by 2041. The impact of these projects spans multiple sectors, including transport, energy, communication, and industrial development, positioning them as essential components of the national development agenda.
However, the success of these mega projects depends heavily on timely and efficient execution. Delays in completion not only affect the projected economic benefits but also lead to cost overruns, decreased investor confidence, and missed opportunities for trade and industry.
The Padma Bridge: A Case Study of Success and Struggle
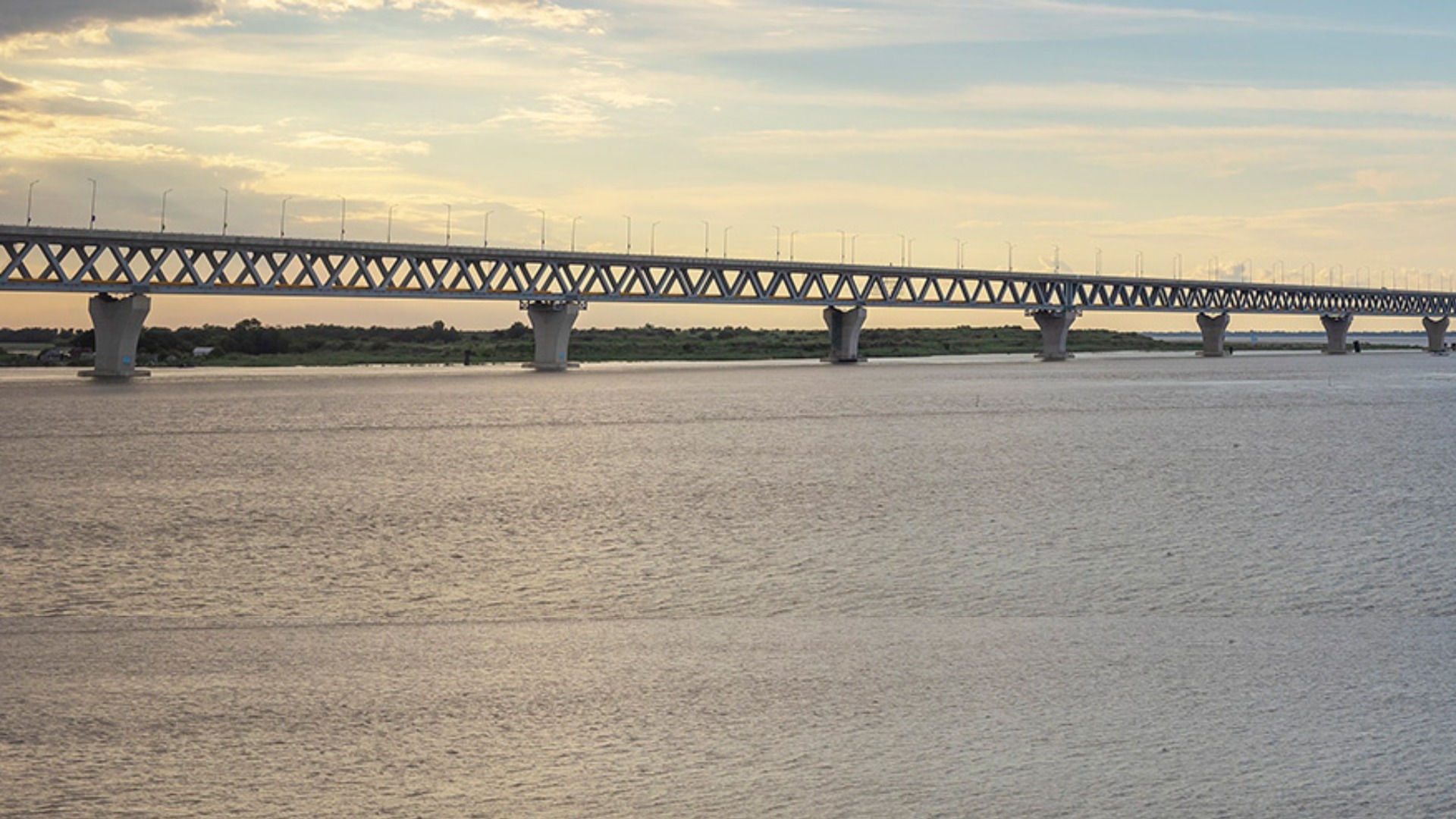
The Padma Bridge, Bangladesh’s most significant infrastructure achievement to date, was inaugurated in June 2022 after years of delays, cost escalations, and challenges. Initially slated for completion in 2014, the project was delayed for several reasons, including allegations of corruption, financing issues after the World Bank withdrew funding, and technical challenges related to the bridge’s construction over a highly volatile river system. Despite these obstacles, the government persevered, securing alternative financing and completing the project using domestic funds.
The completion of the Padma Bridge is expected to boost GDP by 1.2%, improve connectivity between the capital and the southwest region of the country, and facilitate trade with neighboring countries. However, the extended timeline and cost overruns (the project cost ballooned from an estimated $3 billion to nearly $4 billion) serve as a cautionary tale for other mega projects in the country.
Other Delayed Mega Projects: Current Status and Challenges
Several other key mega projects in Bangladesh are currently experiencing delays, which have raised concerns about their timely completion and overall feasibility.
1. Dhaka Metro Rail Project
The Dhaka Metro Rail project, intended to alleviate Dhaka’s notorious traffic congestion, was initially scheduled to be completed by 2021. However, the project has faced numerous delays, primarily due to procurement issues, the COVID-19 pandemic, and land acquisition disputes. As of 2023, partial sections of the metro rail have been opened, but the full project is still behind schedule. These delays have resulted in cost escalations and public frustration, as the city continues to grapple with severe traffic problems.
2. Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant
The Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant, a joint venture between Bangladesh and Russia, is another crucial project aimed at addressing the country’s energy crisis. Initially expected to be operational by 2023, the project has faced delays due to technical and logistical challenges, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and global supply chain disruptions. The delays in Rooppur have had significant repercussions on Bangladesh’s energy sector, which continues to struggle with electricity shortages and rising demand.
3. Payra Deep Sea Port
The Payra Deep Sea Port, envisioned as a game-changer for Bangladesh’s maritime trade, has also faced delays. The project, aimed at enhancing the country’s shipping and export capabilities, was expected to be completed by 2021. However, land acquisition problems, environmental concerns, and inadequate financing have significantly slowed progress. The delay in completing this project has hindered the country’s ability to capitalize on its strategic geographic position for international trade.
4. Matarbari Power Plant
The Matarbari coal-fired power plant, part of Bangladesh’s broader plan to enhance energy security, has seen significant delays due to land acquisition problems and environmental opposition. The project, which is crucial for addressing the country’s chronic electricity shortages, has also experienced cost overruns, putting additional pressure on the national budget.
Causes of Delays in Mega Projects
The delays in Bangladesh’s mega projects are attributable to several interrelated factors:
- Land Acquisition and Resettlement Issues: Land acquisition remains a persistent problem for most large-scale infrastructure projects in Bangladesh. Prolonged negotiations, disputes over compensation, and the need to resettle displaced communities have delayed many projects, leading to extended timelines and increased costs.
- Financing and Budget Constraints: Securing adequate financing for these projects has been a challenge, particularly in cases where international funding agencies, like the World Bank, have withdrawn support. Domestic funding often faces limitations, and cost overruns strain the national budget.
- Political and Administrative Bureaucracy: The bureaucratic red tape involved in large-scale projects often leads to inefficiencies, with approval processes being slow and cumbersome. Corruption and political interference further complicate project management and execution.
- Technical and Logistical Challenges: The complex technical nature of many mega projects, particularly those involving advanced engineering, leads to frequent delays. Moreover, Bangladesh’s infrastructure development capacity, particularly in terms of skilled labor and technical expertise, is still developing.
- Environmental and Social Concerns: Environmental regulations and concerns about the impact of projects on local communities have also contributed to delays. Projects like the Matarbari Power Plant and Payra Deep Sea Port have faced opposition from environmental activists, leading to additional legal and regulatory hurdles.
The Economic Impact of Delays
The economic implications of delays in mega projects are profound. Cost overruns and extended timelines increase the financial burden on the government and reduce the projected return on investment. Furthermore, delays hinder the economic benefits that these projects are intended to provide, such as improved connectivity, enhanced trade, and increased energy security. This, in turn, affects investor confidence, as international and domestic stakeholders become hesitant to invest in projects that are perceived as risky or inefficient.
The Way Forward: Overcoming Challenges
To overcome the challenges of mega project delays, the government and relevant authorities need to adopt a more strategic approach to project management. This could include:
- Strengthening Institutional Capacity: Building the technical and managerial capacity of institutions responsible for overseeing mega projects is essential. This would ensure that projects are planned and executed more efficiently.
- Streamlining Bureaucratic Processes: Simplifying the approval process for projects and reducing bureaucratic delays could significantly speed up implementation. Anti-corruption measures should also be strengthened to ensure transparency in project management.
- Improving Land Acquisition Processes: Developing a more transparent and fair system for land acquisition, with adequate compensation and timely resettlement of displaced communities, would help reduce delays.
- Enhancing Financing Mechanisms: The government could explore alternative financing mechanisms, such as public-private partnerships (PPPs) and international bonds, to ensure that funding is available for mega projects.
While mega projects like the Padma Bridge have demonstrated Bangladesh’s potential for transformative infrastructure development, delays in other projects highlight the significant challenges that remain. Addressing these delays is crucial for ensuring that the country can fully realize the economic and social benefits of these large-scale investments. By adopting more efficient project management practices and addressing the root causes of delays, Bangladesh can continue on its path toward sustainable growth and development.
 A.B.M. Abir
A.B.M. Abir