The reign of Yazid Ibn Muawiya is an important and controversial chapter in the history of Islam. Yazid Ibn Muawiyah was the son of Muawiyah Ibn Abu Sufyan, the founder of the Umayyad Caliphate. His reign (681-683 AD) marks an example of despotism and instability in Islamic history. Yazid’s reign is remembered not only for political turmoil, but also for his policies and actions, which had a profound impact on later Islamic politics. This report will analyze various aspects of Yazid’s dictatorship and discuss the long-term effects of his rule.
Yazid Ibn Abu Sufyan was a companion of Muhammad. In 634, Caliph Abu Bakr RA. Four generals were sent by Yazid Ibn Abu Sufyan to conquer Roman Syria. After the conquest of Damascus he was appointed as the governor of Damascus. He led the left wing of the Muslim army in the Battle of Yarmouk. He is the brother of Khalifa Hazrat Muawiya.
The context of Yazid’s rise to power
Yazid ibn Mu’awiya’s rise to power was on the one hand a family transfer of power, on the other hand it ushered in a new chapter in Islamic politics. After the death of Muawiya ibn Abu Sufyan, Yazid was chosen as his successor. Yazid’s rise to power was largely based on favoritism from his father’s side and a strong military. However, this process was not through direct popular elections, making Yazid’s rule unacceptable and controversial.
The reign of Yazid: Major events and policies
Yazid’s reign began in a difficult political and military environment. Some notable events took place during his reign that became symbols of his tyranny and cruelty:
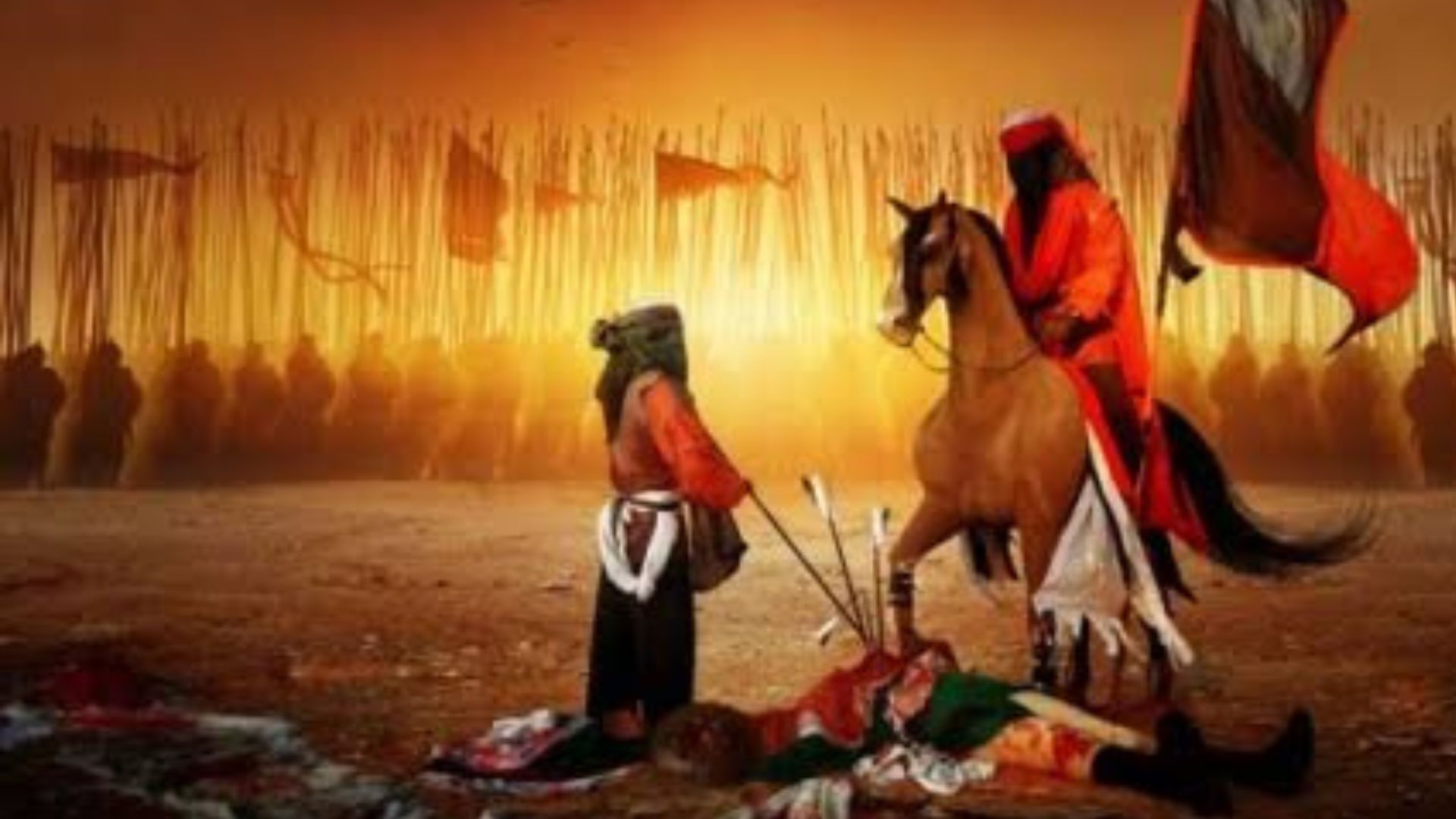
Imam Hussain’s Rebellion: A prime example of Yazid’s tyranny during his rule is the Karbala revolution led by Imam Hussain (RA). Imam Hussain stood against Yazid to defend the basic principles of Islam. As a result of this revolt, Imam Hussain and his family were brutally killed by Yazid’s forces, which became a tragic event in Islamic history.
Centralization of Umayyad rule: Yazid reduced the independence of local rulers by centralizing his power. This leads to increased corruption and instability within the administrative system. The powers of local leaders are tightly controlled and their local autonomy is curtailed, leading to increased discontent among the local population.
Policy of Political Repression: Yazid took drastic measures to suppress his political opponents. Opposition was suppressed through political imprisonment, torture, and assassination. Yazid adopted a harsh attitude towards opponents and used force against them.
Analysis of Yazid’s rule
The analysis of Yazid’s rule is a complex and important process, which helps to determine the various aspects of tyranny and its impact in Islamic history. The reign of Yazid ibn Mu’awiya (681-683 AD) is considered a controversial chapter in Islamic history. An analysis of his rule can be discussed mainly in a few key aspects:
Centralization of power
During his rule, Yazid took various steps to centralize power. Yazid’s rise to power after the death of Muawiya ibn Abu Sufyan was largely through family succession, not popular election. Yazid established a centralized administrative system to establish his power, which reduced the independence of local rulers and favored centralization of power.
**Internal Resistance**: Centralization of power causes local rulers to lose influence and discontent among local populations. Limitation of powers of local rulers and instability of administrative system lead to social unrest.
Political repression
Yazid took various drastic measures to suppress the political opposition. Instead of tolerating political opposition, he used force, resulting in a regime contrary to democratic values.
Karbala Conflict: The Karbala Revolution led by Imam Hussain was a major challenge to Yazid’s rule. Yazid showed brutality against Imam Hussain and his family members in the Karbala conflict, which is a shining example of the autocracy of his rule.
Political Imprisonment and Torture: Yazid endured imprisonment, torture and killing of opposition political leaders. These actions are the manifestation of his dictatorship and the violation of the human rights of the people.
Unethical activities
Under Yazid’s rule various unusual and unjust activities were conducted. These activities were against Islamic principles and indicated inhumane treatment of common people.
Religious Violence: Yazid increased religious violence during his rule. He showed a lack of religious adherence and respect for Islamic principles, which became a serious concern for Islamic society.
Military Campaigns: Yazid tried to maintain his power through military campaigns and invasions. These operations undermine the internal security of the country and create unrest in the lives of the common people.
Social and religious influences
Yazid’s reign had a long-term impact on Islamic society. As a result of his autocracy and repression, various changes and reactions were initiated in the society.
Religious Changes: Yazid’s rule influenced changes in religious values. The Karbala Revolution is considered an important milestone in Islamic history and it influenced the re-evaluation of religious values.
Social unrest: Social unrest increased under Yazid rule. Political and religious tensions rose during his reign, creating divisions in Islamic society.
Evaluation of history
In order to assess the history of Yazid’s rule, it is important to understand the impact of his rule and the subsequent context. The despotism and social unrest created by his rule can be considered an important lesson in Islamic history. After Yazid’s rule, new trends emerged in Islamic politics and religious and social values changed.
**Historical and Ethical Analysis**
An in-depth analysis of the impact of Yazid’s reign should be provided, which would help explain the impact of his rule on society and the subsequent changes in Islamic politics. The political and social unrest that resulted from Yazid’s rule had a profound effect on Islamic society:
1. **Social Unrest**: Social unrest increases under Yazid rule. His rule led to a decline in public faith in Islamic principles and created discord among religious groups. Events such as the Karbala Revolution ushered in massive social changes among the masses, which became an important chapter in Islamic history.
2. **Political Impact**: Yazid’s reign had a long-term impact on Islamic politics. His despotism and violence later led to the emergence of new trends in Islamic politics. Political repression and centralization of power lead to instability and conflict in society.
Religious Changes: Yazid’s reign was also an era of religious changes. After the Karbala Revolution, a new perspective on religious values emerged in Islamic society. Imam Hussain’s martyrdom became an important part of Islamic tradition and culture and is an example of increasing public confidence in religious values.
Historical analysis
Yazid’s reign is considered a controversial chapter in Islamic history. His reign (681-683 AD) had a profound impact on Islamic politics in many ways.
Political instability and centralization of power: Yazid’s rule is an example of centralization of power. His reign was an attempt to usurp political power by the elite class. Centralization of power reduces the independence of local rulers and creates political instability in different regions.
Karbala Revolution: A major historical event of Yazid rule is the Battle of Karbala. The Karbala Revolution led by Imam Hussain (RA) is considered a major protest against Yazid tyranny. The conflict led to worldwide criticism of the Yazidi regime’s inhumanity and torture policies.
Immoral Activities and Military Campaigns: Yazid ruled his reign with military campaigns and violence. Under his rule, political power was retained in various regions through military operations, which is considered an example of power instability and violence in history.
Political Impact: Yazid’s rule ushered in new trends in Islamic politics. As a result of political repression and autocracy under his rule, new structural changes in Islamic politics followed, such as unrest and reaction between the Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates.
Ethical analysis
Ethical analysis of Yazid’s rule evaluates the humane and moral aspects of his rule. The ethical aspects of Yazid rule may be particularly contemplated:
Human Rights Violations: Yazid’s rule was a period of human rights violations. Under his rule, brutality and torture were applied against political opponents. Imam Hussain and his family were killed in the Karbala conflict, which was seen as a violation of human rights.
Autocracy and Moral Decay: Yazid’s rule is a clear example of autocracy. Under his rule there was moral decay in the administrative and political system. Disempowerment of local leaders and oppression of them was morally questionable.
biography
Yazid Ibn Abu Sufyan was the son of Abu Sufyan Ibn Harb and the brother of the first Caliph Muawiyah. Caliph Yazid Ibn Muawiyah and Yazid Ibn Abu Sufyan are not the same person.
Yazid ibn Abu Sufyan was one of the four generals sent by Caliph Abu Bakr to conquer Roman Syria in 634. After the conquest of Damascus he was appointed as the governor of Damascus. He led the left wing of the Muslim army in the Battle of Yarmouk. After the death of Abu Ubaydah ibn al-Zarrah from the plague in 639, Mu’adh ibn Jabal became governor of Syria. Mu’az also died of the plague. Then Caliph Umar Ibn al-Khattab appointed Yazid as the governor of Syria. He too died of the plague in 640.
Yazid’s dictatorship is a controversial chapter in Islamic history. The changes and unrest caused by his rule in Islamic society are still relevant today. The response to Yazid’s regime can be considered a lesson from today’s perspective, proving the importance of speaking out against tyranny.
After Yazid’s rule, the changes and turmoil that took place in Islamic politics and society is an important lesson in today’s context. This chapter of history is not just an incident of the past, but a lesson for the present and the future.
 Md. Ibrahim Hossain Bishal
Md. Ibrahim Hossain Bishal