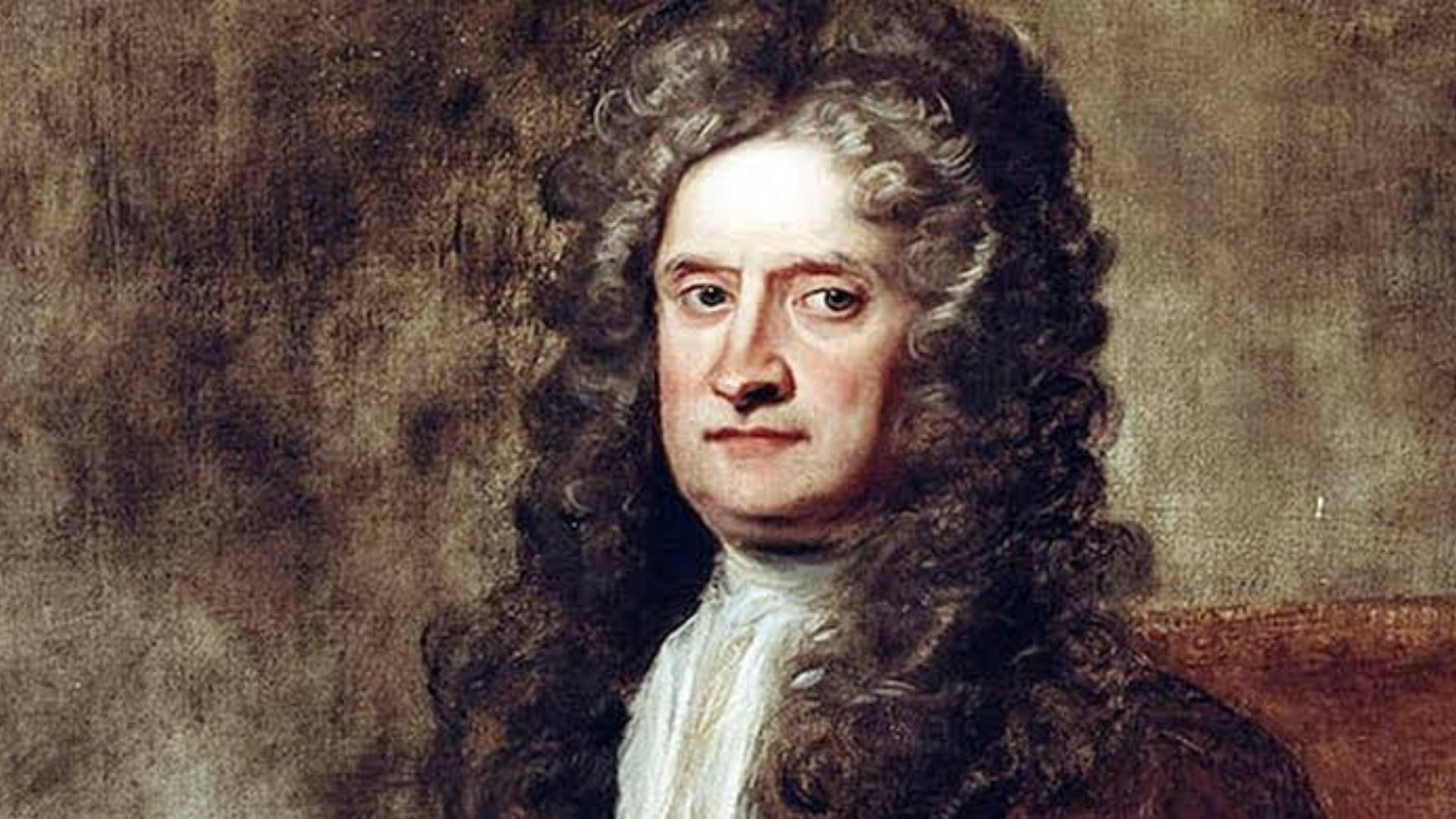
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) was one of the iconic figures of modern science and mathematics. His work ushered in a scientific revolution and redefined the fundamental concepts of physics. Newton’s theories and discoveries had a profound impact on many branches of science, including motion, gravitation, calculus, and optics.
Early childhood and education
Isaac Newton was born on 25 December 1642 in the village of Linste (Lincolnshire) in England in a farming family. His father, Isaac Newton Sr., was a farmer and died just three months after his birth. Newton’s mother, Hannah Newton, married a second time during his childhood and left Newton with his Missington family.
Newton had an ordinary childhood, but received his primary education at Killingworth. Newton was very curious as a child and showed his talent in elementary school. In 1655, he entered Trinity College, Cambridge University. At Cambridge he began to delve into physics, mathematics, and other scientific subjects.
Beginning of research and scientific work at Cambridge
While studying at Cambridge, Newton was influenced by the work of Roger Bacon, Galileo Galilei, and Kepler. During the plague epidemic of 1665–66, when Cambridge University was closed, Newton returned to his village home and completed much of his important work during this period. It was during this period that Newton laid the fundamental foundations of scientific thought.
1. Calculus:**
Newton developed the basic concepts of calculus. Although Leibniz also expressed the basic concepts of calculus at the same time, Newton’s calculus provided a new approach to mathematical analysis and problem solving. Newton’s concept of calculus played an important role in later mathematical research.
2. Laws of Motion and Force:**
Newton established his laws of motion and force, published in ‘Principia Mathematica’ (1687). Newton’s third law, “for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”, became a fundamental concept in physics. Newton’s second law, “The rate of change of motion of an object is proportional to the external force acting on it”, establishes the fundamental laws of motion and force in the universe.
3. Gravitational Theory:**
Newton established the theory of gravitation, which states that all objects have an attractive force towards each other. According to his theory, this gravitational force is expected to be proportional to the mass of the objects and inverse to the square of the distance between them. This theory plays an important role in understanding the motion and structure of the universe.
Principia Mathematica: The Beginning of the Scientific Revolution
Newton’s ‘Principia Mathematica’ was published in 1687. This book established the fundamental laws of physics and laid the foundation for the scientific revolution. Newton’s theory of gravitation and laws of motion and force opened new horizons in scientific research.
1. Implications of Gravitational Theory:**
Newton’s theory of gravitation provides an accurate explanation of the vastness of the universe and the motions of the planets and stars. His theory explains the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the motion of the other planets. Newton’s theory provided a fundamental basis for the theory of gravitation and is considered a cornerstone of modern physics.
2. Natural Philosophy and Scientific Method:**
Newton’s work had an important influence on the method of scientific research. Through his fundamental laws and theories, he developed scientific research methods and experimental techniques. Newton’s scientific method led to the establishment of scientific theories based on evidence and results through observation, calculation and experiment.
Calculations, optics, and other tasks
Newton also made significant contributions to calculus, optics, and other fields during his lifetime.
1. Count:**
Through Newton’s theory of calculus, he provided new methods for fundamental mathematical analysis and problem solving. Through calculation, he was able to solve a variety of mathematical problems and it later became a powerful tool in scientific research.
2. Optics:**
Newton did important work in optics. In his research, he proved that white light splits into different colored components. Newton studied the process of scattering and reflection of light and elaborated on these subjects in ‘Optics’. His research contributed to the development of fundamental theories of optics.
3. Chemistry and Metallurgy:**
Newton also did some work in chemistry and metallurgy. Although his work was mainly focused on physics, he studied the properties of matter and chemical reactions. His works later made important contributions to the fields of chemistry and metallurgy.
Career in later life
Towards the end of his life, Newton served as President of the Royal Society of London. While in this position, he encouraged scientific research and development and formulated various standards and norms for the scientific community.
**1. Working as Revenue Officer:**
Newton was appointed revenue officer in 1696. During his tenure he oversees monetary policy and various administrative matters. His work gives him the opportunity to contribute to the development of the economic policy of the country.
**2. Religious and Philosophical Thoughts:**
Newton was also active in religious and philosophical thought. He delves deeply into religious texts and Christian doctrine and writes on fundamental philosophical issues. His religious and philosophical works are considered complementary to his scientific thinking.
Newton’s death and legacy
Isaac Newton died on March 20, 1727 in London. After his death, his work and ideas helped bring about a revolutionary change in scientific research. The impact of Newton’s work laid the foundation for modern science, and his theories and ideas are still considered the cornerstones of scientific research today.
**1. Newton’s Place in Scientific History:**
Newton’s work established the foundation of modern science. His scientific theories and concepts are still relevant today and are considered the cornerstones of scientific research. Newton’s work provided a new understanding of the world from a scientific perspective and served as an inspiration to scientists and researchers.
**2. Newton’s Place in Scientific History:**
Newton’s work established the foundation of modern science. His scientific theories and concepts are still relevant today and are considered the cornerstones of scientific research. Newton’s work provided a new understanding of the world from a scientific perspective and served as an inspiration to scientists and researchers.
**3. Newton’s Influence on Modern Science:**
The influence of Newton’s theories can be seen in various branches of modern science. His laws of motion and gravitation play a very important role in contemporary physics. His contributions to computation, optics, and other scientific research are still used as the foundation of research today.
**4. Newton’s Personal Life and Character:**
Newton’s personal life and character are also related to his scientific contributions. His efficiency, innovative thinking, and extraordinary analytical abilities have earned him a unique place in the scientific world. His disposition, concentration, and keen interest in research ensured the excellence of his scientific work.
Newton’s death and legacy (remains)
**3. Newton’s Personal Life and Character:**
Newton’s personal life was quite mysterious. He was devoted exclusively to his research and often isolated from society and ordinary life. Concentration and confidence in his scientific work kept him engaged with a kind of focus and enthusiasm. Newton’s character had a deeply contemplative attitude, reflecting his depth of scientific thought and analytical ability.
**4. Newton’s Place in Scientific History:**
The influence of Isaac Newton’s work spans every branch of modern science. His theories of motion, gravitation, and computation are still considered fundamental scientific ideas. Newton’s work laid the foundation for modern physics and helped bring about fundamental changes in many branches of scientific research.
**5. Newton’s contribution:**
Newton’s theories and discoveries brought fundamental changes in scientific thought. His laws of motion and gravitation provide us with a powerful approach to understanding the motion and structure of the universe. His contributions to computation and optics played an important role in the mathematical analysis and understanding of the nature of light.
**6. Newton’s Influence on Modern Science:**
Newton’s theories have had a profound impact on many branches of modern science. His theory of computation provided a fundamental approach to mathematical analysis and solving scientific problems. His research in optics provided new insights into the nature of light, and his theory of gravitation laid a fundamental foundation for understanding the motion and structure of the universe.
Isaac Newton was one of the most iconic figures in modern science and mathematics. His theories of computation, optics, and gravitation sparked scientific revolutions and laid the foundation for modern science. Newton’s theory and research opened new horizons in scientific thinking and his work is still recognized today as a cornerstone of scientific research.
Newton’s three famous laws of motion are:
A stationary object wants to stay at rest forever and an object in motion wants to stay in uniform motion forever unless an external net force is applied to it. (Also known as Law of Inertia)
The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the force applied on it and the momentum changes in the direction of the applied force. Mathematically it is written as:F→=dp→dt=ddt(mv→)=v→dmdt+mdv→dt.The first term vanishes if mass is kept constant. Denoting the acceleration as a→=dv→/dt gives the famous equation: F→=ma→, from which we know, “The acceleration of an object is proportional to the magnitude of the total force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.”
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. That is, F1=−F2
Newton’s contributions were not limited to physics; His work also had a profound influence on mathematics, optics, and philosophical thought. Through his work, scientists have gained new insights into the motion, force, and nature of light in the universe. Newton’s theories opened a new chapter in scientific thinking and his research provided a strong foundation for future scientific thinking.
Analysis of Newton’s life teaches us how a concentration and innovative thinking can revolutionize the scientific world. His contributions are still regarded as seminal pieces of scientific research and his name will be remembered forever.
 Md. Ibrahim Hossain Bishal
Md. Ibrahim Hossain Bishal