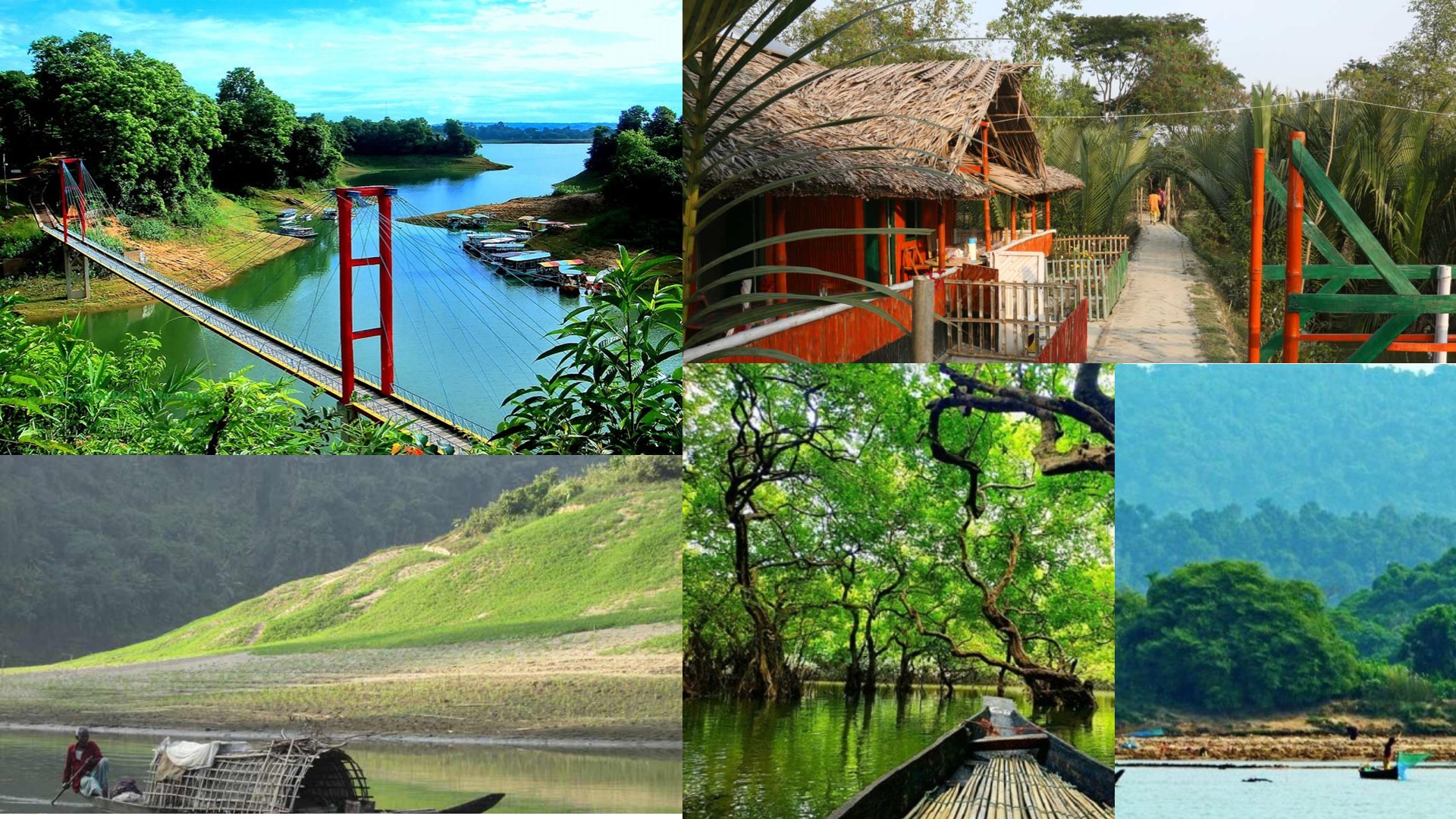
Bangladesh, a country rich in natural beauty, cultural diversity, and historical significance, has seen its tourism industry flourish in recent years. From the pristine beaches of Cox’s Bazar to the lush greenery of the Sundarbans, Bangladesh offers a wide range of attractions that draw both domestic and international tourists. However, as the industry grows, so does the need for sustainable tourism practices that ensure long-term environmental, social, and economic viability. Sustainable tourism, which emphasizes the careful management of resources and the active involvement of local communities, is increasingly recognized as essential for the future of Bangladesh’s tourism sector.
The Significance of Sustainable Tourism in Bangladesh
Sustainable tourism is crucial for countries like Bangladesh, where rapid industrialization and urbanization often lead to environmental degradation and social disparities. The tourism industry has the potential to significantly boost the economy, but without sustainable practices, it can also contribute to environmental damage, cultural erosion, and economic inequality. Sustainable tourism addresses these issues by promoting responsible travel that conserves the environment, respects local cultures, and generates economic benefits for local communities.
1. **Environmental Conservation**: One of the most pressing concerns in Bangladesh’s tourism industry is the need for environmental conservation. The country is home to some of the world’s most unique and fragile ecosystems, including the Sundarbans, the world’s largest mangrove forest, and the hill tracts of Chittagong. These areas are not only vital for biodiversity but also act as natural barriers against climate change impacts, such as rising sea levels and cyclones. However, increasing tourist footfall in these regions has led to issues like pollution, deforestation, and habitat destruction. Sustainable tourism practices, such as eco-tourism, can mitigate these impacts by encouraging tourists to minimize their environmental footprint, supporting conservation efforts, and promoting the use of renewable resources.
2. **Cultural Preservation**: Bangladesh is a mosaic of cultures, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and customs. From the indigenous communities in the Chittagong Hill Tracts to the diverse cultural practices in Sylhet, preserving this cultural heritage is vital for the identity of the nation. Tourism can play a significant role in this preservation by fostering a greater appreciation for these cultures among visitors. However, without sustainable practices, there is a risk that tourism could lead to the commodification or dilution of cultural traditions. Sustainable tourism seeks to protect and promote cultural heritage by involving local communities in the tourism process, ensuring that cultural practices are presented authentically, and educating tourists about the importance of respecting local customs and traditions.
3. **Economic Empowerment**: Tourism has the potential to drive economic growth in Bangladesh, particularly in rural and underdeveloped areas. By providing jobs and generating income, the tourism industry can help lift communities out of poverty. However, for this economic benefit to be truly sustainable, it must be inclusive. This means ensuring that the economic gains from tourism are distributed equitably among all stakeholders, including local communities. Sustainable tourism promotes this by encouraging local ownership of tourism-related businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, and tour companies, and by ensuring that a significant portion of the revenue generated from tourism stays within the local economy. Additionally, sustainable tourism can create opportunities for local artisans, farmers, and entrepreneurs to sell their products and services to tourists, further boosting the local economy.
The Role of Local Communities in Sustainable Tourism
The success of sustainable tourism in Bangladesh hinges on the active participation and empowerment of local communities. These communities are not only the custodians of the natural and cultural resources that attract tourists but also the primary beneficiaries of sustainable tourism practices. Involving local communities in the planning and management of tourism activities ensures that their voices are heard, their needs are met, and their livelihoods are protected.
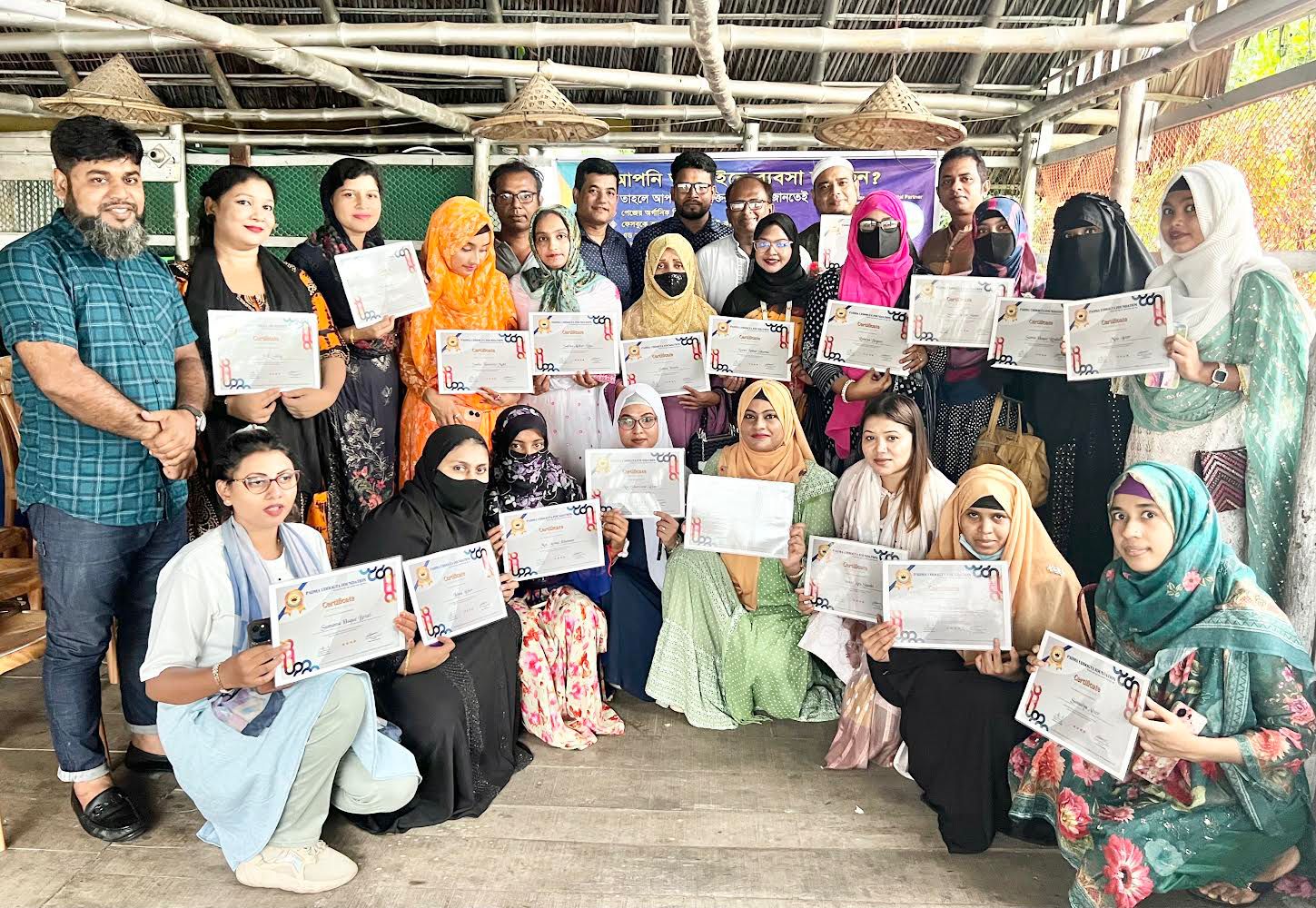
1. **Community Participation and Empowerment**: One of the core principles of sustainable tourism is the empowerment of local communities. This involves giving local people a stake in the tourism industry and involving them in decision-making processes. When communities are actively involved in tourism, they are more likely to support conservation efforts, protect their cultural heritage, and ensure that tourism benefits are equitably distributed. Empowerment can take many forms, from providing training and education to helping local entrepreneurs start and grow tourism-related businesses. For example, in the Sundarbans, community-based eco-tourism initiatives have been successful in involving local communities in tourism activities, such as guiding, accommodation, and handicraft production. These initiatives not only provide income but also help raise awareness about the importance of conserving the Sundarbans’ unique ecosystem.
2. **Capacity Building and Education**: Building the capacity of local communities to participate in and benefit from tourism is essential for sustainable development. This includes providing training in areas such as hospitality, customer service, environmental management, and business skills. Education is also crucial for raising awareness about the benefits and challenges of tourism and for promoting responsible tourism practices. For example, educating local communities about the importance of waste management and resource conservation can help reduce the environmental impact of tourism. Similarly, training in cultural interpretation can help locals present their heritage in a way that is both authentic and engaging for tourists.
3. **Innovative Local Initiatives**: Local communities are often best positioned to develop innovative tourism initiatives that reflect their unique cultural and natural assets. These initiatives can include community-run eco-lodges, cultural heritage tours, and locally-produced handicrafts and food products. Such initiatives not only provide a source of income for local people but also enhance the tourist experience by offering authentic, place-based experiences. For instance, in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, indigenous communities have developed cultural tourism products, such as traditional dance performances and handicraft workshops, which allow tourists to engage directly with local culture while providing much-needed income for the communities.
4. **Sustainable Livelihoods**: Ensuring that tourism provides sustainable livelihoods for local communities is a key aspect of sustainable tourism. This means that tourism-related jobs and businesses should offer fair wages, safe working conditions, and opportunities for advancement. It also means that tourism should not displace traditional livelihoods, such as farming or fishing, but rather complement and enhance them. For example, in rural areas of Bangladesh, agri-tourism initiatives have been developed where tourists can stay on working farms, learn about traditional farming practices, and even participate in activities such as planting or harvesting. This not only provides an additional source of income for farmers but also helps preserve traditional agricultural practices and promotes food security.
Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Tourism in Bangladesh
While the potential for sustainable tourism in Bangladesh is immense, there are several challenges that must be addressed to fully realize this potential. These challenges include inadequate infrastructure, environmental degradation, lack of awareness and education, and insufficient investment in sustainable tourism initiatives. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth.
1. **Infrastructure Development**: One of the major challenges facing the tourism industry in Bangladesh is the lack of adequate infrastructure, particularly in remote and rural areas. Poor road conditions, limited transportation options, and insufficient accommodation facilities can all deter tourists from visiting certain destinations. Addressing these infrastructure challenges is crucial for the growth of sustainable tourism. This can include improving roads, expanding public transportation networks, and developing eco-friendly accommodation options. For example, the development of sustainable lodges and eco-resorts in key tourist areas can provide high-quality accommodation for tourists while minimizing environmental impact.
2. **Environmental Management**: Environmental degradation is a significant challenge in many of Bangladesh’s tourist destinations. Issues such as pollution, deforestation, and habitat destruction can all undermine the long-term sustainability of tourism. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach to environmental management, including enforcing environmental regulations, promoting responsible tourism practices, and investing in conservation efforts. For example, initiatives such as the cleanup of Cox’s Bazar beach and the reforestation of degraded areas in the Sundarbans can help restore these ecosystems and ensure their long-term viability as tourist destinations.
3. **Awareness and Education**: Lack of awareness and education about sustainable tourism practices is another challenge in Bangladesh. Many tourists and tourism operators are not fully aware of the environmental, social, and economic impacts of tourism. Raising awareness and providing education about sustainable tourism practices is essential for promoting responsible tourism. This can include public awareness campaigns, educational programs in schools and communities, and training for tourism operators. For example, educational programs that teach tourists about the importance of conserving water, reducing waste, and respecting local cultures can help promote more sustainable tourism practices.
4. **Investment in Sustainable Tourism**: Insufficient investment in sustainable tourism initiatives is a significant barrier to the growth of this sector in Bangladesh. This includes both public and private investment in infrastructure, conservation, and community-based tourism projects. Encouraging investment in sustainable tourism requires creating an enabling environment that includes clear policies and regulations, financial incentives, and support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). For example, providing low-interest loans or grants for eco-tourism projects, offering tax incentives for sustainable tourism businesses, and supporting public-private partnerships can all help attract investment in sustainable tourism.
The Future of Sustainable Tourism in Bangladesh
The future of sustainable tourism in Bangladesh looks promising if the right strategies and initiatives are implemented. By prioritizing environmental conservation, cultural preservation, and community empowerment, Bangladesh can develop a tourism industry that is not only economically viable but also socially and environmentally responsible.
1. **Strategic Planning and Policy Development**: Developing a comprehensive national tourism strategy that prioritizes sustainability is essential for guiding the growth of the tourism industry in Bangladesh. This strategy should include clear goals and objectives, as well as specific actions to promote sustainable tourism practices. It should also include measures to monitor and evaluate the impact of tourism on the environment, culture, and local communities. Additionally, developing policies that support sustainable tourism, such as environmental regulations, zoning laws, and incentives for sustainable businesses, can help create an enabling environment for sustainable tourism.
2. **Partnerships and Collaboration**: Building partnerships and collaborations between the government, private sector, civil society, and local communities is essential for the success of sustainable tourism
in Bangladesh. These partnerships can help mobilize resources, share knowledge and expertise, and coordinate efforts to promote sustainable tourism. For example, partnerships between the government and local communities can help develop community-based tourism initiatives, while collaborations between the private sector and conservation organizations can support environmental protection efforts.
3. **Innovation and Technology**: Embracing innovation and technology is key to advancing sustainable tourism in Bangladesh. This includes using technology to improve the efficiency and sustainability of tourism operations, such as through the use of renewable energy, waste management systems, and digital platforms for booking and information sharing. Innovation can also drive the development of new tourism products and experiences that are both sustainable and appealing to tourists. For example, the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) can provide immersive experiences that allow tourists to explore cultural and natural heritage sites in a low-impact way.
4. **Capacity Building and Skills Development**: Investing in capacity building and skills development for local communities, tourism operators, and government officials is essential for the long-term sustainability of the tourism industry. This includes providing training in sustainable tourism practices, environmental management, customer service, and business skills. It also involves developing educational programs that promote a culture of sustainability and responsibility among tourists, tourism operators, and local communities. By building the capacity of all stakeholders, Bangladesh can ensure that its tourism industry is equipped to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Sustainable tourism represents a path forward for Bangladesh’s tourism industry, offering a way to balance economic growth with environmental conservation, cultural preservation, and social equity. By involving local communities, promoting responsible tourism practices, and investing in sustainable infrastructure and initiatives, Bangladesh can develop a tourism industry that not only attracts visitors but also enhances the well-being of its people and the health of its environment. The journey towards sustainable tourism is challenging, but with strategic planning, collaboration, and innovation, Bangladesh can position itself as a global leader in sustainable tourism and ensure a bright future for its tourism industry.
 A.B.M. Abir
A.B.M. Abir