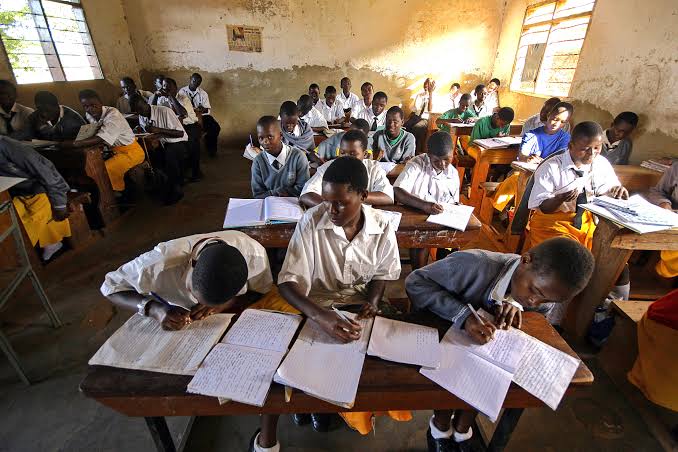
Africa is a continent of immense diversity, rich cultural heritage, and substantial economic potential. However, despite notable progress in recent years, the continent continues to face significant challenges in its education sector. Millions of children remain out of school, educational resources are often inadequate, and the quality of education varies significantly across different regions. To address these issues, African countries have begun to leverage technology in innovative ways to improve access to education, enhance learning outcomes, and bridge the education gap.
This report explores the new initiatives in Africa’s education sector, focusing on the use of technology and its impact. It discusses various technological interventions, their successes, challenges, and future potential in transforming education across the continent.
Current Challenges in Africa’s Education Sector:
Africa’s education system faces several persistent challenges that have hindered progress toward achieving universal education and improving educational outcomes.
Some of the key issues include:
1. Limited Access to Education: Many children in Africa, particularly in rural and conflict-affected areas, still lack access to quality education. According to UNESCO, around 100 million children and adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa are not in school. Distance, poverty, gender inequality, and conflict are some of the factors contributing to this issue.
2. Inadequate Infrastructure and Resources: Many schools in Africa lack basic infrastructure, such as electricity, clean water, and proper sanitation. Additionally, there is a severe shortage of trained teachers, textbooks, and learning materials. Overcrowded classrooms and poor learning environments are common in many regions.
3. Quality of Education: The quality of education in Africa varies significantly, with many students not acquiring basic literacy and numeracy skills. Poorly trained teachers, outdated curricula, and a lack of effective teaching methods contribute to low learning outcomes.
4. High Dropout Rates: Many students in Africa drop out of school due to economic pressures, cultural norms, early marriage, child labor, or a lack of motivation due to poor educational quality. This contributes to high dropout rates and low completion rates, particularly at the secondary education level.
5. Impact of COVID-19: The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated existing challenges in Africa’s education sector. School closures, lack of access to digital devices, and limited internet connectivity have disrupted learning for millions of children.
To tackle these challenges, African countries have increasingly turned to technology as a key enabler of educational reform. Technology offers innovative solutions to expand access to education, improve teaching and learning, and enhance administrative efficiency. Below are some of the key ways technology is being used in Africa’s education sector:
1. Digital Learning Platforms and E-Learning: The adoption of digital learning platforms and e-learning tools has been a significant trend in Africa’s education sector. These platforms provide interactive learning materials, videos, quizzes, and assessments, which can be accessed online or offline. Countries like Kenya, South Africa, Nigeria, and Rwanda have developed national digital learning platforms to provide quality educational content to students in remote areas.
2. Mobile Learning (mLearning): With high mobile penetration rates across Africa, mobile learning has emerged as a popular solution for delivering education. Mobile apps, SMS-based learning tools, and mobile-optimized websites are being used to deliver lessons, distribute learning materials, and provide real-time feedback. For example, Eneza Education in Kenya offers SMS-based learning content to students in rural areas, enabling them to learn even without internet access.
3. Remote Learning During Crises: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many African countries adopted remote learning solutions, such as radio and television broadcasts, to reach students who were unable to attend school. In Nigeria, for example, the government launched the “Learn at Home” program, which provided lessons via radio, television, and online platforms to ensure continuity of learning during school closures.
4. EdTech Startups and Innovation Hubs: Africa has witnessed a surge in educational technology (EdTech) startups and innovation hubs that are developing solutions to address specific educational challenges. Startups like Andela, uLesson, and Kukua are creating platforms, apps, and tools that offer personalized learning experiences, digital content, and skills development opportunities.
5. AI and Adaptive Learning Technologies: Artificial intelligence (AI) and adaptive learning technologies are being introduced to provide personalized learning experiences tailored to individual students’ needs. These technologies analyze students’ performance and adjust the content and pace of learning accordingly. For example, in South Africa, the Siyavula platform uses AI to provide personalized math and science lessons based on each student’s performance.
6. Blended Learning Models: Many African schools and institutions are adopting blended learning models that combine traditional classroom teaching with digital tools and online resources. This approach allows for more interactive and engaging learning experiences while making education more accessible to students in remote areas.
Several technology-driven initiatives have been successfully implemented across Africa, demonstrating the potential of digital solutions in transforming education. Below are some notable success stories:
1. Bridge International Academies (Kenya, Uganda, Nigeria): Bridge International Academies is a network of low-cost private schools that use technology to deliver quality education to underserved communities. Teachers use tablet computers loaded with digital lesson plans, and students learn through a combination of digital and traditional methods. Bridge has improved learning outcomes, with students consistently outperforming their peers in national exams.
2. Eneza Education (Kenya): Eneza Education is a mobile-based learning platform that offers lessons, quizzes, and assessments via SMS to students in rural and remote areas. The platform has reached over 6 million students across Kenya, Tanzania, and Ghana, providing them with affordable access to quality educational content.
3. Moringa School (Kenya): Moringa School is a technology education institution that offers coding boot camps and digital skills training programs. It focuses on bridging the skills gap in Africa by providing students with hands-on training in software development, data science, and other tech-related fields. Moringa School has trained thousands of students and successfully placed them in tech jobs both locally and internationally.
4. The iMlango Project (Kenya): The iMlango Project, funded by the UK government, is an initiative aimed at improving learning outcomes in rural primary schools in Kenya through digital learning resources. The project provides internet connectivity, digital content, and data analytics tools to enhance teaching and learning. It has reached over 180,000 students in 245 schools, improving literacy and numeracy outcomes.
5. Tuteria (Nigeria): Tuteria is an online platform that connects students with qualified tutors for personalized learning in various subjects. It uses technology to facilitate learning and make education more accessible to students across Nigeria. Tuteria has successfully helped thousands of students improve their academic performance and acquire new skills.
The use of technology in Africa’s education sector has led to several notable achievements and positive impacts:
1. Increased Access to Education: Technology has played a critical role in expanding access to education, particularly for students in remote and underserved areas. Digital learning platforms, mobile learning tools, and online resources have made education more accessible to a broader audience.
2. Improved Learning Outcomes: Several technology-driven initiatives have demonstrated improvements in learning outcomes, particularly in literacy and numeracy. Digital platforms that offer interactive content, quizzes, and assessments have helped students better understand and retain information.
3. Enhanced Teacher Training and Support: Technology has enabled more effective teacher training and professional development programs. Online courses, webinars, and digital resources provide teachers with access to new teaching methods, curricula, and tools to improve their effectiveness in the classroom.
4. Increased Engagement and Motivation: Digital tools and interactive content have made learning more engaging and motivating for students. Gamification, multimedia content, and interactive exercises help maintain students’ interest and encourage active participation in learning.
5. Support for Remote and Crisis Learning: The use of technology has been instrumental in supporting remote learning during crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. It has enabled students to continue learning despite school closures and other disruptions.
Challenges and Barriers to Technology-Driven Education in Africa:
While technology has brought significant benefits to Africa’s education sector, several challenges and barriers need to be addressed to fully realize its potential:
1. Digital Divide and Inequitable Access: There is a significant digital divide in Africa, with disparities in access to digital devices, internet connectivity, and electricity. Many rural and low-income communities lack the infrastructure needed to support technology-driven education.
2. Cost and Affordability: The cost of digital devices, internet access, and e-learning tools can be prohibitive for many African families and schools. High data costs and limited affordability remain significant barriers to widespread adoption.
3. Lack of Digital Literacy and Skills: Limited digital literacy among students, teachers, and parents can hinder the effective use of technology in education. Capacity building and training are needed to ensure that all stakeholders can effectively use digital tools and platforms.
4. Inadequate Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Many African countries lack comprehensive policies and regulatory frameworks to support the integration of technology in education. Clear guidelines, standards, and support mechanisms are needed to ensure the effective and sustainable use of technology in schools.
5. Cultural Resistance and Perceptions: In some communities, there is resistance to the use of technology in education due to cultural beliefs, fears about privacy and security, or skepticism about the effectiveness of digital tools.
6. Sustainability and Scalability: Many technology-driven initiatives in Africa face challenges related to sustainability and scalability. Ensuring long-term funding, maintaining infrastructure, and scaling successful projects to reach a wider audience require concerted efforts and strategic planning.
Future Prospects and Recommendations:
To further harness the potential of technology in transforming Africa’s education sector, several key actions and strategies should be considered for the future:
1. Investing in Digital Infrastructure: Expanding internet connectivity, particularly in rural and remote areas, should be a priority. Governments, private sector partners, and international organizations need to collaborate on investments in digital infrastructure, such as broadband networks, electricity access, and affordable digital devices. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can play a crucial role in bridging the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to technology.
2. Promoting Affordable Access to Digital Tools and Resources: To make technology-driven education accessible to all, there must be efforts to lower the costs of digital devices, internet data, and educational software. Governments could consider subsidizing the cost of devices for low-income families or partnering with tech companies to provide affordable or free digital tools to schools.
3. Enhancing Digital Literacy and Skills Development: Comprehensive training programs should be developed to build digital literacy skills among students, teachers, and parents. Incorporating digital literacy into school curricula, offering regular professional development for educators, and providing community-based training programs can help ensure that all stakeholders are equipped to use technology effectively.
4. Developing Inclusive and Relevant Digital Content: Educational content needs to be culturally relevant, multilingual, and inclusive to cater to the diverse needs of African students. Local content creators, educators, and technology developers should be encouraged to produce high-quality digital learning materials that reflect the unique contexts of different communities. Additionally, integrating indigenous knowledge, local languages, and culturally relevant examples can make learning more engaging and effective.
5. Establishing Robust Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Governments should develop clear policies and regulatory frameworks to support the integration of technology in education. This includes setting standards for digital learning tools, ensuring data privacy and security, promoting open educational resources (OER), and providing guidelines for effective implementation. Policies should also focus on inclusivity, ensuring that girls, children with disabilities, and other marginalized groups have equal access to technology-based education.
6. Encouraging Public-Private Partnerships and Innovation: To drive innovation and scalability, governments should encourage partnerships with the private sector, NGOs, and international organizations. These collaborations can provide technical expertise, funding, and resources to develop and scale innovative EdTech solutions. Establishing innovation hubs, accelerators, and incubation programs can also foster the growth of EdTech startups and drive technological advancements in the education sector.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation for Continuous Improvement: It is important to establish systems for monitoring and evaluating the impact of technology-driven education initiatives. Continuous assessment of program outcomes, student performance, and learning experiences can help identify areas for improvement, scale successful models, and ensure that resources are being used effectively. Data-driven decision-making will be key to optimizing the use of technology in education.
8. Building Resilience for Future Crises: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for resilience in the education sector. Governments and institutions should develop contingency plans and build flexible learning models that can quickly adapt to disruptions, such as natural disasters, pandemics, or political instability. This includes investing in digital infrastructure, creating diverse learning pathways, and promoting remote and hybrid learning models.
The use of technology in Africa’s education sector has shown immense potential to address many of the continent’s longstanding educational challenges. From increasing access to education in remote areas to enhancing learning outcomes through personalized and engaging content, technology is revolutionizing how education is delivered across Africa. The success stories of EdTech initiatives in countries like Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, and Rwanda underscore the transformative power of digital solutions in education.
However, significant challenges remain, including the digital divide, cost barriers, limited digital literacy, and the need for supportive policies. To fully harness the potential of technology, African countries must continue to invest in digital infrastructure, promote inclusive and affordable access to digital tools, build capacity among educators and students, and foster an environment that encourages innovation and public-private collaboration.
By addressing these challenges and building on existing successes, Africa can create a more equitable, inclusive, and resilient education system that prepares its young population for the demands of the 21st century. The continued adoption and integration of technology will be critical to achieving this vision and ensuring that every child in Africa has the opportunity to receive a quality education. As Africa moves forward, the focus should remain on creating sustainable, scalable, and impactful technology-driven solutions that meet the diverse needs of its students and communities.
This transformation will not only enhance educational outcomes but also contribute to broader social and economic development, empowering the next generation to realize their full potential and drive Africa’s growth in the years to come.
 Md. Anas Ebna Arfin (Nibir)
Md. Anas Ebna Arfin (Nibir)